Background
The global emergence of multi-drug resistant bacterial infections has resulted in enormous costs and has become a major threat to public health. About seventy percent of nosocomial infections are resistant to at least one commonly use antibiotic. Pactamycin is a structurally unique aminocyclitol antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces pactum. Its promising antitumor, antiviral, and anti-protozoal activities make pactamycin a promising parent compound for drug development that shows potent antimicrobial activity. Unfortunately, its development as a clinical compound has been hampered by its wide-ranging cytotoxicity. Moreover, its complex chemical structure has rendered its structural modification via synthetic organic chemistry difficult.
Technology Description
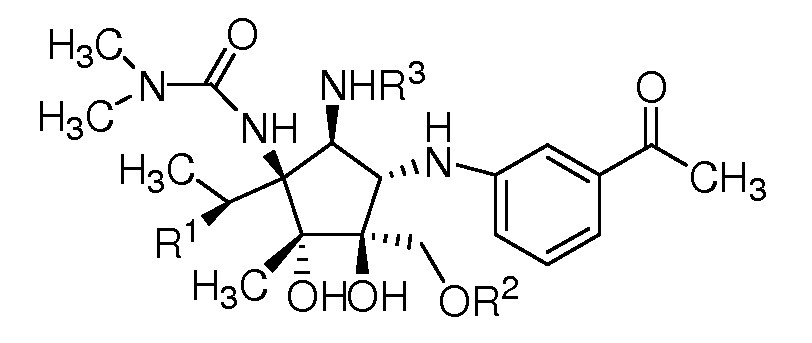
Patented (US8957251) pactamycin analogs having antibacterial, antitumor, antiviral and antimalarial activity. Also patented are biosynthetic methods of producing both the identified and additional new analogs. The identified analogs and methods of biosynthetic production provide a promising opportunity for discovery and development of new antibacterial, antimalarial, and antitumor drugs.
Related publications by lead inventor, Dr. Taifo Mahmud:
1. Mutasynthesis of Fluorinated Pactamycin Analogs and Their Antimalarial Activity
2. Pactamycin Analogs with Improved Selectivity toward Malarial Parasites
3. Deciphering Pactamycin Biosynthesis and Engineered Production of New Pactamycin Analogues
Features & Benefits
- Antimalarial agents show increased selectivity for malarial parasites
- Biosynthetically produced
- Decreased toxicity
Applications
- Antibacterial
- Antimalarial
- Antitumor
Status
Patented US 8,957,251 B2