Works by detecting gamma-rays from the surrounding area and generating an energy spectrum based on the readings
Background
Gamma ray spectrometers are an essential part of labs, hospitals, power plants, and any other situation where there is a risk of exposure to gamma ray radiation. Gamma ray exposure increases the risk of cancer, and can cause genetic mutations and radiation sickness. However, modern gamma ray spectrometers are expensive, unwieldy, and require a large amount of power to use. Therefore, there is a significant role in radiation safety that can be played by a compact, low-cost, low-power gamma ray radiation detector. Researchers at Oregon State University have developed a gamma ray spectrometer prototype intended to fill precisely this role.
Technology Description
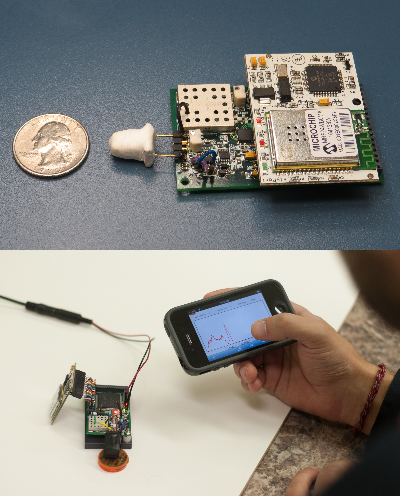
The gamma ray spectrometer works by detecting gamma-rays from the surrounding area and generating an energy spectrum based on the readings. A mobile phone can access the device wirelessly in order to display the data (Figure below). It possesses different modes that allow for low power operation. As a result of being inexpensive and compact, the prototype is mass-producible, with options for alternate configurations based on customer needs.
Features & Benefits
- Inexpensive
- Compact
- Can operate on low power modes
Applications
- Radiation mapping
- Battlefield assessment
- Medical dose monitoring
Opportunity
Prototype has been built, seeking development partners.
Status
US Patent No. 10,031,242