Carbon-based materials for efficient, inexpensive, and tunable micro-LED display applications
Background
Micro light emitting diode (micro-LED) display is emerging as a candidate to drive a new generation of display technology. LED-based light sources are also widely used in lighting applications. It remains a challenge to develop cost-effective color conversion micro-LED technologies with enhanced light emission efficiency and minimized excitation light leakage through its color conversion layer. Carbon dots are also an emerging material for micro-LEDs as an alternative to more expensive quantum materials, some of which are toxic due to the presence of cadmium or other heavy metals. However, carbon dots remain difficult to produce with consistent size distribution, improved quantum yield, and tunable emission color, especially in the longer wavelengths of the visible spectrum (i.e., orange and red). This technology addresses these challenges.
Technology Description
Researchers at Oregon State University have developed a new micro-LED utilizing carbon quantum dots that have strong excitation in the blue spectrum with tunable emission at high quantum efficiency in the orange and red, independent of excitation wavelength. The micro-LED structure also has negligible leakage of excitation light in the UV or blue through the color conversion layer, making these devices suitable for next generation high resolution displays without the use of toxic heavy metals.
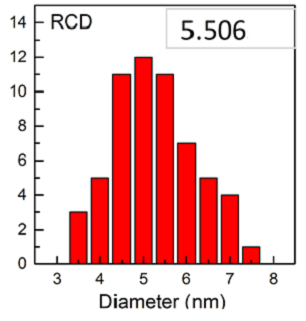
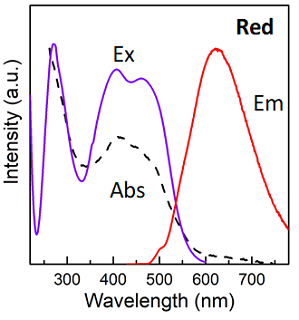
Size distribution of red emission carbon quantum dots excitation and emission spectra
Features & Benefits
- Low excitation leakage
- Environmentally friendly
- Enhanced red color
Applications
- Light emitting devices or sensors
- Fluorescence labeling in biosensors
- Electronic displays
Opportunity
OSU is seeking development partners to improve the technology readiness level (TRL) and commercialize.
Status
Patent US 17/648,419